AutoCAD Tips & Tricks
Today's Tip
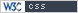
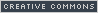
Bring recent commands to the command line with the "Up" cursor key
Use the "Up" cursor (arrow) key on the keyboard to scroll through recently used commands on the command line. When you find the one you want, hit the Enter key to start that command.
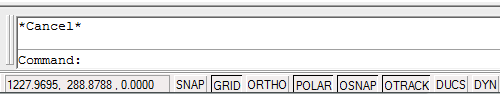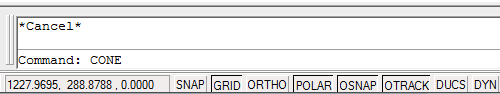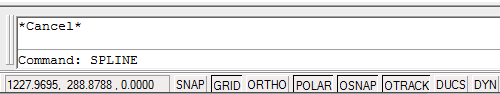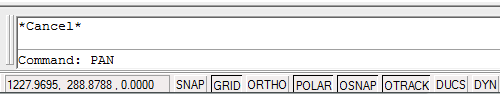
You can also use the "Down" cursor key to scroll in the oposite direction.
Yesterday's Tip
Salvage a corrupted drawing
So, you opened a drawing only to find it has been corrupted. You've tried Recover but to no avail. Now what?
As a last resort, open a new drawing and then insert the corrupted drawing into the new one (). The insertion will only bring in the main (Model Space) components of the corrupted drawing; this trick does not recover any paper space objects. Hey, I didn't promise a miracle but it sure beats losing the drawing altogether now, doesn't it?.
Monday's Tip
Repeat for Efficiency
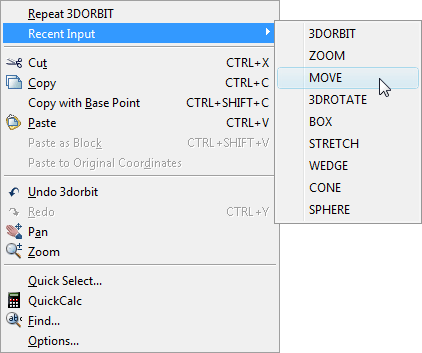 Sometimes, you may find yourself having to use the same command repeatedly. This can be a pain, unless you are aware that the previous command can always be repeated by hitting the Enter key on the keyboard or by using the right-click mouse button and selecting the name of the command you just used. Both these methods are more efficient than repeatedly finding a command on a toolbar or from a pull-down menu.
Sometimes, you may find yourself having to use the same command repeatedly. This can be a pain, unless you are aware that the previous command can always be repeated by hitting the Enter key on the keyboard or by using the right-click mouse button and selecting the name of the command you just used. Both these methods are more efficient than repeatedly finding a command on a toolbar or from a pull-down menu.
What's more annoying than having to repeat a single command (and more common) is having to repeat a sequence of maybe two or three commands. Obviously, you can't use the "Enter to repeat" trick. However, the right-click menu has another option that can help in these situations. Below the name of the last command used, is a menu option that says . If you select this option, you will see a list of all the commands used in the current drawing session, with the most recently used at the top.
Using this method, you can repeat any sequence of commands without having to return to a toolbar or pull-down menu.
Note: This function is controlled by the INPUTHISTORYMODE variable.
Sunday's Tip
Clear that 3D clutter with Orbit
When 3D drawings get complicated, it may become difficult to view a particular object in your drawing because it's being crowded by other objects. Here's a neat trick that will help you solve this problem.
Select the object or objects you're interested in before starting the Orbit (3DORBIT) command. When you start the Orbit command, all the other objects in the drawing will become invisible and your selected object can be seen alone. The other objects become visible again as soon as you exit from Orbit.
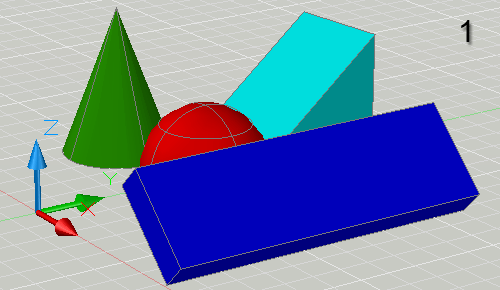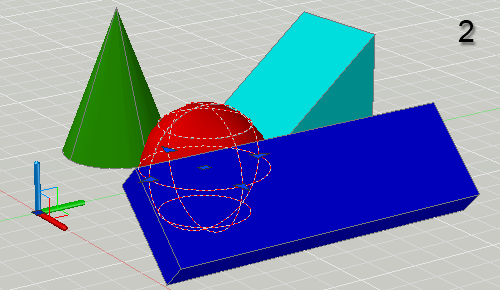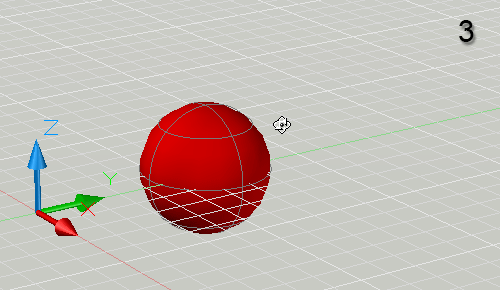
This technique can also be used to ensure that the selected object always appears in the center of the scene when orbiting. It is also possible to select the center point of rotation without having the other objects disappear - use the 3DORBITCTR command.
Saturday's Tip
Command line in a window (F2)
The command line can be very useful, especially for beginners because AutoCAD often gives useful prompts which helps when learning how to use some of the more complicated commands. The command line is also used by AutoCAD to report information back to the user, but sometimes that information may run to several lines of text, and disappear from view. A good example of this is the Distance command (you can run this from the keyboard by typing DIST). The problem is that by default, the command line is only two lines high and so if you use the Distance command, you don't even see the distance reported to the command line.
One way round this problem is to increase the depth of the command line to show more lines but this takes up valuable drawing area. A better solution is to display the command window using the F2 key on the keyboard.
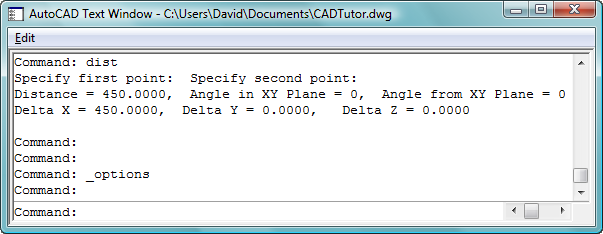
As you can see above, the command window also allows you to scroll back through the command line so that you can review your recent drawing history.
Friday's Tip
Trim Up
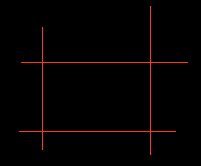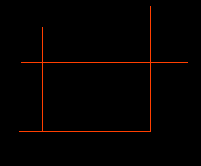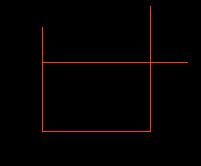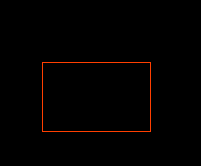 Often, you find yourself using the Trim command to tidy up loose ends of lines. If this is the case, don't bother selecting cutting edges, just use the "select all" option.
Often, you find yourself using the Trim command to tidy up loose ends of lines. If this is the case, don't bother selecting cutting edges, just use the "select all" option.
Start the Trim command, from the pull-down menu or TRIM from the command line. At the prompt, simply hit ![]() (Enter) to accept the <select all> option.
(Enter) to accept the <select all> option.
Now, just pick the line ends you want to remove.
Thursday's Tip
Offset to the current layer
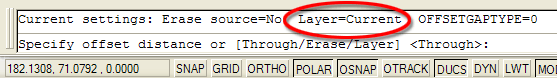 When you use the offset command, the new object always ends up on the same layer as the source object. That's the default option but you can have objects offset to the current layer.
When you use the offset command, the new object always ends up on the same layer as the source object. That's the default option but you can have objects offset to the current layer.
Start the Offset command, from the pull-down menu or OFFSET from the command line. At the prompt, enter L for "Layer" and then C for "Current". Now, each time you use Offset, objects will be created on the current layer.
To set Offset back to the default, use the same sequence but enter S for "Source".
Tutorials of the Moment
The most recently viewed tutorials
Optimisation and Workflow
|
All About Shadows
|
|
Last visited: 1 minute ago |
Last visited: 1 minute ago |
|
Modifying Objects
|
The Material Editor
|
|
Last visited: 2 minutes ago |
Last visited: 4 minutes ago |
Local Navigation
Tutorials
Helping you to learn more of the skills you need, for free.
Featured Tutorial:
AutoCAD 2010: 3D Scale & 3D Align
CADTutor tutorials are comprehensive lessons, designed to give you a deeper understanding.
Total tutorials: 108
Sponsored Links