All Activity
- Past hour
-
JerryFiedler started following Updated AISC Shapes for STL.LSP
-

Updated AISC Shapes for STL.LSP
JerryFiedler replied to gtwatson's topic in AutoLISP, Visual LISP & DCL
@Jgrand3371 I just loaded the app onto my BrisCAD Pro V26 and it appears to work. I just tested a few of the many options, certainly not an extensive test. This program is great! @gtwatson Thank you for sharing. - Today
-
nkh503 joined the community
-
Steven P started following Vehicle Tracking - where to find details for vehicles
-
Vehicle Tracking - where to find details for vehicles
Steven P replied to Adam - Inspire's topic in Autodesk Software General
Going to resurrect an old thread.... Going to have to do some vehicle tracking this week or next, articulated lorry but extended trailer. I have a PDF of the dimensions. Is there an easy to follow guide out there that shows what values to put where to convert a CAD drawing into a vehicle tracked vehicle? Thanks (My first attempts this morning had the trailer pointing out the front, cutting the driver in half). I guess I can work it out trial and error but jumping that part. And second question which is my default model for new tools, does anyone have an x wing fighter modelled as a 'vehicle'? That might be a weekend thing. Thanks -
KStag started following Like component tags batch update
-
I currently am struggling with this issue. There are many ways to update all component attributes within the drawing I'm in. ATTOUT/ATTIN works great for updating all of the necessary information within the active drawing. However, it does not push this update throughout the project to the other instances of the same component tags. I am not sure if this is the correct place to ask for assistance, but I need help figuring out how to force an update to the rest of the project based on the information in the current drawing. Otherwise I have to edit every single component on one drawing, and then utilize task list to update the other drawings, or I have to update every single drawing with ATTOUT/ATTIN. I'm looking for something that would allow a bulk edit of each tags attributes that will also sync project wide.
-
KStag joined the community
-
- 10 comments
-
- 1
-

-
Biana_058 joined the community
-
Danielm103 started following Python, A Very high performance Delaunay triangle algorithm and Python, a high-performance concave hull
-
https://github.com/mapbox/concaveman https://github.com/sadaszewski/concaveman-cpp it’s not automatic in that it requires parameters depending on the point distribution. concavity: A relative measure of concavity. A value of 1 provides a detailed shape, while Infinity results in a convex hull. lengthThreshold: Determines the minimum segment length considered for further detailing, with higher values leading to simpler shapes. Chomped through this 280k point set import traceback from pyrx import Ap, Db, Ed, Ge # --- Command for PyRx --- @Ap.Command() def doit0(): try: ps, ss = Ed.Editor.select([(Db.DxfCode.kDxfStart, "POINT")]) pnts = Ge.Point3dArray([Db.Point(id).position() for id in ss]) hull_points = pnts.concaveHull(0.8, 100) db = Db.curDb() pl = Db.Polyline(hull_points) pl.setDatabaseDefaults() pl.setClosed(True) pl.setColorIndex(2) db.addToModelspace(pl) except Exception: traceback.print_exc()
-
- 1
-

-

Python, A Very high performance Delaunay triangle algorithm
Danielm103 replied to Danielm103's topic in .NET, ObjectARX & VBA
This is a great guide working with Delaunator. https://mapbox.github.io/delaunator/ It explains the relationship between half-edges and triangles. in short the triangles are created in an order, you can iterate the triangles while being aware of the adjacent triangles. A [-1] in the half edge list means that edge is on the outside hull. -

Python, A Very high performance Delaunay triangle algorithm
Danielm103 replied to Danielm103's topic in .NET, ObjectARX & VBA
The algorithm is fast because it returns a list of indexes, to your original array, of the points that make up the triangle, it also returns a list of half edges from pyrx import Ap, Db, Ed, Ge, Gi import traceback @Ap.Command() def doit(): try: filter = [(Db.DxfCode.kDxfStart, "POINT")] ps, ss = Ed.Editor.selectPrompt( "\nSelect points: ", "\nRemove points: ", filter ) if ps != Ed.PromptStatus.eNormal: return pnts = Ge.Point3dArray([Db.Point(id).position() for id in ss]) d = Ge.Delaunator(pnts) print(d.triangles()) print(d.halfedges()) except Exception: print(traceback.format_exc()) [0, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 4, 3, 2, 0] [8, -1, 11, -1, 6, 10, 4, -1, 0, -1, 5, 2] -

Python, A Very high performance Delaunay triangle algorithm
Danielm103 posted a topic in .NET, ObjectARX & VBA
the sample import traceback from time import perf_counter from pyrx import Ap, Db, Ed, Ge # Ge.Delaunator uses a modified version of https://github.com/abellgithub/delaunator-cpp. # Its modified in that it’s designed to use a collection of Ge.Point3d. # its documented here https://mapbox.github.io/delaunator/ # Also see https://github.com/mapbox/delaunator, https://github.com/HakanSeven12/Delaunator-Python # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # Module: PyRx Voronoi & Delaunator Tools # Description: Provides AutoCAD commands to generate Voronoi diagrams # (using Circumcenters and Centroids) and Delaunay triangulation # with contour line generation. # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- print("added command pyvoronoiCCM") print("added command pyvoronoiCEN") print("added command pydelaunator") # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # Helper Functions # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- def do_select(): """ Prompts the user to select AutoCAD POINT entities. Returns: Ed.SelectionSet: The selected set if successful, None otherwise. """ # Define a filter to only select POINT entities filter = [(Db.DxfCode.kDxfStart, "POINT")] # Prompt user for selection and removal # Returns (PromptStatus, SelectionSet) ps, ss = Ed.Editor.selectPrompt("\nSelect points: ", "\nRemove points: ", filter) if ps == Ed.PromptStatus.eNormal: return ss return None def circumcenter(a: Ge.Point3d, b: Ge.Point3d, c: Ge.Point3d): """ Calculates the circumcenter of a triangle defined by three points. The circumcenter is the center of the circle that passes through all three vertices. It is calculated using vector algebra (barycentric coordinates). Args: a (Ge.Point3d): First vertex b (Ge.Point3d): Second vertex c (Ge.Point3d): Third vertex Returns: Ge.Point3d: The circumcenter of the triangle. """ ac: Ge.Vector3d = c - a ab: Ge.Vector3d = b - a # Cross product of AB and AC abXac = ab.crossProduct(ac) # Vector calculation for the circumcenter # Formula: (|AC|^2 * (AB x (AB x AC)) + |AB|^2 * ((AB x AC) x AC)) / (2 * |AB x AC|^2) cc = ( abXac.crossProduct(ab) * ac.lengthSqrd() + ac.crossProduct(abXac) * ab.lengthSqrd() ) # Normalize and translate to point A toCircumsphereCenter = cc / (2.0 * abXac.lengthSqrd()) return a + toCircumsphereCenter def centroid(a: Ge.Point3d, b: Ge.Point3d, c: Ge.Point3d): """ Calculates the centroid (geometric center) of a triangle. The centroid is the arithmetic mean position of all the points in the figure. Args: a (Ge.Point3d): First vertex b (Ge.Point3d): Second vertex c (Ge.Point3d): Third vertex Returns: Ge.Point3d: The centroid of the triangle. """ CX1 = (a.x + b.x + c.x) / 3 CX2 = (a.y + b.y + c.y) / 3 CX3 = (a.z + b.z + c.z) / 3 return Ge.Point3d(CX1, CX2, CX3) def triangle(idx: int, d: Ge.Delaunator, pnts: list[Ge.Point3d]): """ Helper to extract the three vertices of a specific triangle from the Delaunator data. Args: idx (int): Index of the triangle in the flat array (every 3rd index is a new triangle). d (Ge.Delaunator): The Delaunator object. pnts (list): List of input points. Returns: list: A list of three Ge.Point3d objects. """ triangles = d.triangles() return [ pnts[triangles[idx + 0]], pnts[triangles[idx + 1]], pnts[triangles[idx + 2]], ] def triangleAtEdge(e: int): """ Determines the index of the adjacent triangle sharing a half-edge. The Delaunator stores triangles in a flat array. Each edge is shared by two triangles. This function calculates the index of the other triangle based on the half-edge index. Args: e (int): The half-edge index. Returns: int: The index of the adjacent triangle. """ if e % 3 == 1: return e - 1 elif e % 3 == 2: return e - 2 return e def get_3dpointds(objs: list[Db.ObjectId]): """ Extracts the 3D position of selected objects. Args: objs (Ed.SelectionSet): The selection set containing POINT entities. Returns: list: A list of Ge.Point3d objects. """ pnts = [] for id in objs: p = Db.Point(id) pnts.append(p.position()) return pnts # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # Voronoi Generation Functions # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- def getVoronoiEdgesCCM(d: Ge.Delaunator, pnts: list[Ge.Point3d]): """ Generates Voronoi edges using the Circumcenter (CCM) method. For every edge shared by two triangles, the circumcenter of each triangle is calculated. The line connecting these two circumcenters is a Voronoi edge. Args: d (Ge.Delaunator): The Delaunator object. pnts (list): List of input points. Returns: list: A list of tuples, where each tuple contains two Ge.Point3d (start, end). """ edges = [] triangles = d.triangles() halfedges = d.halfedges() # Iterate through the flat triangle array (step 3 for each triangle) for i in range(0, len(triangles), 3): tri1 = triangle(i, d, pnts) # Calculate circumcenter of the current triangle p = circumcenter(tri1[0], tri1[1], tri1[2]) # Check each of the 3 edges of the triangle for o in range(3): if halfedges[i + o] != -1: e = halfedges[i + o] nt = triangleAtEdge(e) # Ensure the adjacent triangle exists if nt < len(triangles): tri2 = triangle(nt, d, pnts) q = circumcenter(tri2[0], tri2[1], tri2[2]) edges.append((p, q)) return edges def getVoronoiEdgesCEN(d: Ge.Delaunator, pnts: list[Ge.Point3d]): """ Generates Voronoi edges using the Centroid (CEN) method. Similar to CCM, but uses the geometric centroid of the triangle instead of the circumcenter. Args: d (Ge.Delaunator): The Delaunator object. pnts (list): List of input points. Returns: list: A list of tuples, where each tuple contains two Ge.Point3d (start, end). """ edges = [] triangles = d.triangles() halfedges = d.halfedges() for i in range(0, len(triangles), 3): tri1 = triangle(i, d, pnts) # Calculate centroid of the current triangle p = centroid(tri1[0], tri1[1], tri1[2]) for o in range(3): if halfedges[i + o] != -1: e = halfedges[i + o] nt = triangleAtEdge(e) if nt < len(triangles): tri2 = triangle(nt, d, pnts) q = centroid(tri2[0], tri2[1], tri2[2]) edges.append((p, q)) return edges # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # Contour Generation Functions # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- def interpolate_point(p1, p2, level): """ Linearly interpolates a point on a line segment at a specific Z level. Args: p1 (list): Start point [x, y, z] p2 (list): End point [x, y, z] level (float): The Z elevation to interpolate to. Returns: list: The interpolated point [x, y, z]. """ t = (level - p1[2]) / (p2[2] - p1[2]) return [p1[0] + t * (p2[0] - p1[0]), p1[1] + t * (p2[1] - p1[1]), level] def process_triangle_contours(triangle_points: list[Ge.Point3d], level: float): """ Processes a single triangle to generate contour segments at a specific Z level. Checks which vertices are below and above the level, then interpolates the intersection points on the edges. Args: triangle_points (list): List of 3 points [x, y, z]. level (float): The Z level to generate contours for. Returns: list: A list of interpolated contour points, or None if no intersection occurs. """ points_below = [] points_above = [] for point in triangle_points: if point[2] < level: points_below.append(point) else: points_above.append(point) # No intersection if all points are on one side if len(points_below) == 0 or len(points_above) == 0: return None contour_points = [] # Case 1: One point below, two above -> Interpolate two edges if len(points_below) == 1: p1 = points_below[0] p2, p3 = points_above contour_points = [ interpolate_point(p1, p2, level), interpolate_point(p1, p3, level), ] # Case 2: Two points below, one above -> Interpolate two edges elif len(points_below) == 2: p1, p2 = points_below p3 = points_above[0] contour_points = [ interpolate_point(p1, p3, level), interpolate_point(p2, p3, level), ] return contour_points # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # AutoCAD Commands # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- @Ap.Command() def pyvoronoiCCM(): """ AutoCAD Command: pyvoronoiCCM Generates a Voronoi diagram using Circumcenters. """ try: ss = do_select() if not ss: return t1_start = perf_counter() pnt3ds = get_3dpointds(ss) # Perform Delaunay triangulation d = Ge.Delaunator(pnt3ds) # Generate Voronoi edges for e in getVoronoiEdgesCCM(d, pnt3ds): # Draw the edge using the Graphics API Ed.Core.grDraw(e[0], e[1], 4, 0) t1_stop = perf_counter() print("Elapsed time: {t:.4f}".format(t=t1_stop - t1_start)) except Exception as err: traceback.print_exception(err) @Ap.Command() def pyvoronoiCEN(): """ AutoCAD Command: pyvoronoiCEN Generates a Voronoi diagram using Centroids. """ try: ss = do_select() if not ss: return t1_start = perf_counter() pnt3ds = get_3dpointds(ss) # Perform Delaunay triangulation d = Ge.Delaunator(pnt3ds) # Generate Voronoi edges for e in getVoronoiEdgesCEN(d, pnt3ds): # Draw the edge using the Graphics API Ed.Core.grDraw(e[0], e[1], 3, 0) t1_stop = perf_counter() print("Elapsed time: {t:.4f}".format(t=t1_stop - t1_start)) except Exception as err: traceback.print_exception(err) @Ap.Command() def pydelaunator(): """ AutoCAD Command: pydelaunator Generates Delaunay triangles and contour lines based on point Z values. """ try: ss = do_select() if not ss: return t1_start = perf_counter() pnt3ds = get_3dpointds(ss) # Perform Delaunay triangulation t = Ge.Delaunator(pnt3ds).triangles() # Calculate min/max Z values for contour generation ncontours = 20 z_values = [p[2] for p in pnt3ds] min_z = min(z_values) max_z = max(z_values) step = (max_z - min_z) / ncontours contour_lines = [] # Generate contour lines for each elevation level for level in [min_z + i * step for i in range(1, ncontours)]: for i in range(0, len(t), 3): triangle_points = [pnt3ds[t[i]], pnt3ds[t[i + 1]], pnt3ds[t[i + 2]]] contour_segment = process_triangle_contours(triangle_points, level) if contour_segment: contour_lines.append(contour_segment) db = Db.HostApplicationServices().workingDatabase() model = Db.BlockTableRecord(db.modelSpaceId(), Db.OpenMode.kForWrite) # Draw triangles for i in range(0, len(t), 3): f = Db.Face(pnt3ds[t[i]], pnt3ds[t[i + 1]], pnt3ds[t[i + 2]]) f.setColorIndex(8) # Color 8 is usually White/Light Gray model.appendAcDbEntity(f) # Draw contours segs = [] for contour in contour_lines: segs.append(Ge.LineSeg3d(Ge.Point3d(contour[0]), Ge.Point3d(contour[1]))) # Convert line segments to a CompositeCurve and then to AutoCAD Curve entities ccs = Ge.CompositeCurve3d.createFromLineSeg3dArray(segs) for cc in ccs: dbc = Db.Core.convertGelibCurveToAcDbCurve(cc) dbc.setColorIndex(3) # Color 3 is usually Cyan model.appendAcDbEntity(dbc) t1_stop = perf_counter() print("Elapsed time: {t:.4f}".format(t=t1_stop - t1_start)) except Exception as err: print(err) -
PDF/ JPG file conversion threat.
EleenD03 replied to nidhi singhania's topic in AutoCAD 2D Drafting, Object Properties & Interface
That’s a fair point about the security risks with random online converters. I’ve definitely noticed that some of the free sites get really 'spammy' or trigger browser warnings lately. I usually try to stick to the built-in 'DWG to PDF' plotter in AutoCAD to keep things clean, but if I’m looking for specific educational templates or tracing layouts for the kids to practice with, I've found it's better to use dedicated niche sites rather than generic converters. I recently came across https://nametracingpdf.com/ for some clean practice sheetsit's a good example of getting a direct PDF without having to jump through those 'convert-this-file' hoops that usually carry the malware risks you’re talking about. - Definitely pays to be cautious where you upload your project files! - Yesterday
-
TotalBoundary • Outline creation tool
CraneGuy commented on Debalance's file in Programs and Scripts
I appreciate your response. I even tried calling the number listed on the domain registration! No reply unfortunately. I used all the workarounds prior to finding TB, but the one click nature of it was invaluable. I messaged Lee Mac to see if he was interested in recreating TB...hopefully he'll be interested in adding the WIPEOUT element.- 10 comments
-
No activity for a few years now and no responses on any forums/email, so could be anything. You might try Lee Mac's LISP. Some verticals have the SHRINKWRAP command, if you have the FREE tool pack and Architecture, it has SHRINKWRAP. You could create hatches, then a boundary and delete the hatches or just have them on a Frozen or No Plot layer.
- 10 comments
-
It might help to provide a lot more information. Where did you get the LISP and what version? What exactly is the meaning of "most of my lisp routines work, but this one does not."? Should be some sort of error or doesn't load correctly, etc. if no error shown in CAD, try to run an error checker in your code editor. Do you have everything in a pathed folder?
-
kaedep2210 joined the community
- Last week
-
Thought I had posted this a dcl front end. (defun inputinfo ( / AH:setvals dcl des) (defun AH:setvals ( / ) (if(= (get_tile "Rb1") "1") (setq ztype "S") (setq ztype "D") ) (cond ((= (get_tile "Rb3") "1")(setq extop "F")) ((= (get_tile "Rb4") "1")(setq extop "P")) ((= (get_tile "Rb5") "1")(setq extop "N")) ) (setq extlen (atof (get_tile "val1"))) (princ) ) (setq dcl (vl-filename-mktemp "" "" ".dcl")) (setq des (open dcl "w") ) (foreach x '( "brklines : dialog {" " label =\"Please choose\" ;" " : row {" " : boxed_radio_column {" " width = 23 ;" " label =\"Single or Double\" ;" "spacer_1 ;" " : radio_button {" "key = \"Rb1\";" "label = \"Single\" ;" " }" "spacer_1 ;" " : radio_button {" "key = \"Rb2\";" "label = \"Double\" ;" " }" "spacer_1 ;" " }" " }" " : row {" " : boxed_radio_column {" " width = 23 ;" " label =\"Extend beyond picked points\" ;" "spacer_1 ;" " : radio_button {" "key = \"Rb3\";" "label = \"Fixed\" ;" " }" "spacer_1 ;" " : radio_button {" "key = \"Rb4\";" "label = \"Proportional\" ;" " }" "spacer_1 ;" " : radio_button {" "key = \"Rb5\";" "label = \"None\" ;" " }" "spacer_1 ;" " }" " }" " : row {" ": edit_box {" " label = \"Extension length\" ;" "spacer_1 ;" " width = 25 ;" "key = \"val1\" ;" " edit_width = 10 ;" " edit_limit = 9 ;" " is_enabled = true ;" " allow_accept=true ;" " }" " }" "spacer_1 ;" " ok_cancel ;" " }" ) (write-line x des ) ) (close des) (setq dcl_id (load_dialog dcl)) (if (not (new_dialog "brklines" dcl_id) ) (exit) ) (set_tile "Rb1" "1") (set_tile "Rb3" "1") (set_tile "val1" "50.0") (action_tile "accept" "(AH:setvals)(done_dialog)") (action_tile "cancel" "(done_dialog)(exit)") (start_dialog) (unload_dialog dcl_id) (vl-file-delete dcl) (princ) ) (inputinfo)
-
Jgrand3371 joined the community
-
Updated AISC Shapes for STL.LSP
Jgrand3371 replied to gtwatson's topic in AutoLISP, Visual LISP & DCL
I use this tool on a daily basis, so thank you for the update. I'm testing a trial version of Bricsys and most of my lisp routines work, but this one does not. Has anyone gotten it to work successfully in Bricsys? -
juanjporras joined the community
-
Dimangular-Vertex Macro Error
zaphod replied to zaphod's topic in The CUI, Hatches, Linetypes, Scripts & Macros
My fault for not stating all the angles were to be measured CW or CCW from 0°. -
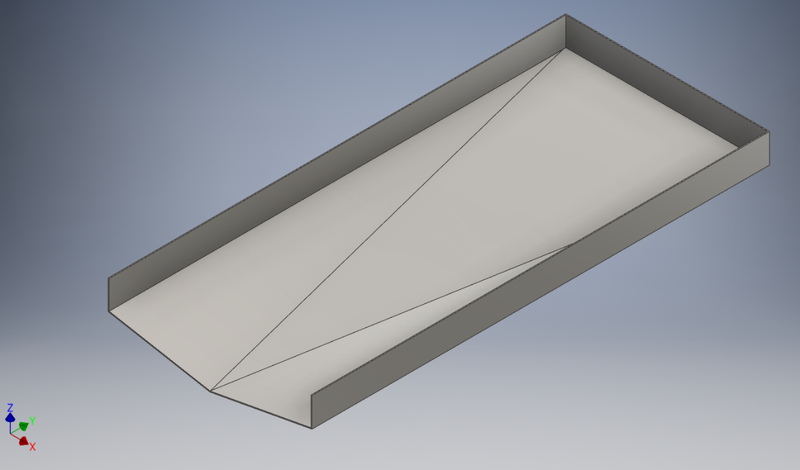
Hi all, I need your help please, to model up a "drip tray" like the one attached, but I need to do it in Inventor Sheet Metal so that I can obtain the flat pattern for laser cutting the material, which is 3mm Stainless Steel. I have done ones that slope to one corner but this one is slightly more complicated, and nothing I try works for me! The below is just an example of the shape, this is modelled form a solid block, which I just cut away the slopes & shelled it out to 3mm thickness. It has 3 slopes on the floor, so that the tray drains to the center at the front. The front plate will be welded on after as at is not possible to fold it as one piece anyway. My efforts involved creating each sloped section of the floor individually (using planes, sketches and faces), and trying to "flange" the vertical sides and then trying to join these up using the bend tool, but it just never works for me. The corners are probably just too complicates with all the different slopes and angles! Any help will be greatly appreciated, and thanks in advance for any help or advice on this. The bottom picture is the desired shape I am looking for as a flat pattern, I have attached a STEP file also Bottom Drip Tray 1460x650x3mm_ST.stp.stpz
-
Denis_B joined the community
-
CraneGuy started following TotalBoundary • Outline creation tool
-
TotalBoundary • Outline creation tool
CraneGuy commented on Debalance's file in Programs and Scripts
- 10 comments
-

Dimangular-Vertex Macro Error
pkenewell replied to zaphod's topic in The CUI, Hatches, Linetypes, Scripts & Macros
Ah Yes - those pesky object snaps getting in the way! What I meant was changing the starting axis from Y (0,0;0,1) to the X axis (0,0;1,0) for angles going CCW within 0 to 90 deg. Sounds like I misunderstood the problem though? -
Dimangular-Vertex Macro Error
zaphod replied to zaphod's topic in The CUI, Hatches, Linetypes, Scripts & Macros
solution from the Autodesk forums "*^C^C^C_dimangular;;non;0,0;non;0,1;\NON" -
Dimangular-Vertex Macro Error
zaphod replied to zaphod's topic in The CUI, Hatches, Linetypes, Scripts & Macros
Indeed, it is sir. Thank you for looking into this issue of mine. Although I'm not certain of what causes the error that I'm seeing, I have the same "Macro" written out on one of my gaming devices, it works, until AutoCAD becomes a dyslexic child. That caused me to look for an "internal" method to AutoCAD. Starting at around 2°, these were my results this morning. Multiple completely different random starting lines. I'm not sure what you mean by changing the start point, I want it to start on the 0° axis from 0,0. I do not use "Dynamic Input" or "Dynamic UCS". -
Saviel joined the community
-

Pathfinding in AutoCAD with the A-Star Algorithm (A*)
Danielm103 replied to heschr's topic in AutoLISP, Visual LISP & DCL
Clever use of safe arrays -
Pathfinding in AutoCAD with the A-Star Algorithm (A*)
ymg3 replied to heschr's topic in AutoLISP, Visual LISP & DCL
As I told you the advantage of this one is only when you have lots of edges and a long path. Acceleration comes from direct access with safearray when fetching value O(1) and replacing the openlist and updating directly in the heap. Mind you this is not a real heap as they have in C++ but probably the best we can do in Autolisp. There might be some optimizing left in the heap specially heap:pop and heap:push ymg -

Pathfinding in AutoCAD with the A-Star Algorithm (A*)
GLAVCVS replied to heschr's topic in AutoLISP, Visual LISP & DCL
Something interesting happens: There's little difference between the execution time of the Lisp version and the FAS version of your new code. And this FAS version isn't much faster than the previous one. The main advantage lies with Lisp. -
Did you contact CADS RC about adding your own lisp programs I would do that as the first step in getting answers. There is some comments in the programming guide about add other lisps. Have you just tried running a lisp by pasting to the command line. (alert (strcat "this dwg name is " (getvar 'dwgname) " and is located at " (getvar 'dwgprefix))) Are you sure its a OEM version of Autocad ? If you type "About" what does it show. Talk to your IT the time savings can be hours a week using lisps, only use LSP files not FAS or VLX. A lsp file is a text file so you can see the code and look for anything that might be dangerous, like vl-file-delete, or only trust people like those here. You can get IT to check any code then add to your company directory location. This has like 130 lisps behind it.
-
rlx started following Use LISP with CADS RC Lite
-
if I read the manual provided by the link from SLW210 you should be able to create and (App)load your own lisp file with your own custom shortcuts (defun c:xx...). Lisp programming interface guide 2.1 Procedure to draw the reinforcement: 1. First draw the outlines with the required dimension. 2. Create a lisp file called demo.lsp in C:\ 3. Copy and paste the code mentioned below to the demo.lsp 4. Save it and close. 5. In AutoCAD use the Appload command to load the demo.lsp 6. Type Demo in the command prompt. It will ask you to pick the Lower Left corner of the base and the upper right corner of the base. Pick points p1 & p2 as mentioned in the drawing. 7. Specify the Cover and Centre to centre spacing. 8. You can see the reinforcement drawn on the screen. 9. Repeat step 6 & 7 for different footing outlines. But I'm just guessing here... never heard of this program so can't really tell. In the old days I smuggled my lisp routines in by creating a *.mnl file so my routines were loaded along with the menu (despite many efforts of a certain human who's name can't be spoken trying to stop users (specifically me) from being able to do their own stuff). Now many years later he admits dragons are very difficult if not impossible to stop (haha). Another way is starting AutoCad with your own custom profile by creating your own desktop shortcut (Google is your friend)